
The factor can be either discrete different machine, different plants, different shifts, etc.
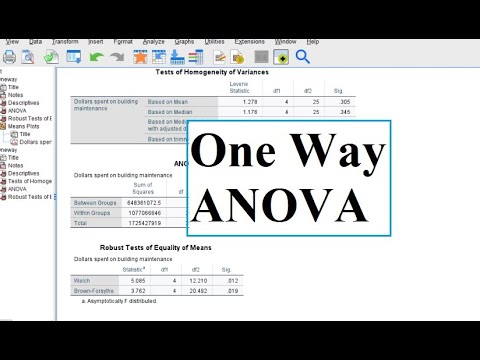
The one-way ANOVA is useful when we want to compare the effect of multiple levels of one factor and we have multiple observations at each level. Finally, it is assumed that the random component can be modeled with a Gaussian distribution with fixed location and spread. We further assume that the fixed deterministic component can be modeled as the sum of an overall mean and some contribution from the factor level. If the F 0 value is significant at a given significance level greater than the cut-off value in a F table, then there is a level effect present in the data.įor estimation purposes, we assume the data can adequately be modeled as the sum of a deterministic component and a random component. It can be shown that given the assumptions about the data stated below, the ratio of the level mean square and the residual mean square follows an F distribution with degrees of freedom as shown in the ANOVA table. However, if there is a level effect, the level mean square will be higher than the residual mean square. Therefore, if there really were no level effect, these two estimates would be just two different ways to estimate the same parameter and should be close numerically. Similarly, if there really were no level effect, the mean square across levels would be an estimate of the overall variance. This works out to be the mean square of the residuals. If we assume that the observations within each level have the same variance, we can calculate the variance within each level and pool these together to obtain an estimate of the overall population variance. The way we do this is by comparing the within-level variancs to the between-level variance. We are testing to see if the observed data support the hypothesis that the levels of the factor are significantly different from each other. Most analysis programs will handle this for you automatically. By applying the constraint that the level effects must sum to zero, we can now obtain a unique solution to the CLM equations.

Since the level effects are just deviations from the grand mean, they must sum to zero. We overcome this problem by applying a constraint to the model. The only problem is that the model is saturated and no unique solution exists. If you look at the model above you will notice that it is in the form of a CLM. The second way to estimate effects is through the use of CLM techniques. The value splitting example illustrates the calculations involved. These can be summarized in a table as shown below and tests can be made to determine if the factor levels are significant. First, we can calculate the total variation, within-level variation and across-level variation. Estimation click here to see details of one-way value splitting.Įstimation for the one-way layout can be performed one of two ways. Finally, we can compare the variation within levels to the variation across levels. We can then look at the deviation of the mean of each level from the grand mean to understand something about the level effects. We can also average the means of each level to obtain a grand mean. The residuals will tell us about the variation within each level. With this kind of layout we can calculate the mean of the observations within each level of our factor. A one-way layout consists of a single factor with several levels and multiple observations at each level. Also, it is important to realize that the one-way ANOVA is an omnibus test statistic and cannot tell you which specific groups were statistically significantly different from each other it only tells you that at least two groups were different.
For example, you could use a one-way ANOVA to understand whether exam performance differed based on test anxiety levels amongst students, dividing students into three independent groups e. The one-way analysis of variance ANOVA is used to determine whether there are any statistically significant differences between the means of two or more independent unrelated groups although you tend to only see it used when there are a minimum of three, rather than two groups.
The hypothesis is based on available information and the investigator's belief about the population parameters. This module will continue the discussion of hypothesis testing, where a specific statement or hypothesis is generated about a population parameter, and sample statistics are used to assess the likelihood that the hypothesis is true. File Name: one way anova example problems and solutions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
